Lumbar canal stenosis
Symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis
Patients with this disorder cannot walk a long distance without a break. The most common symptom is intermittent claudication in which patients have to take a rest repeatedly when walking. In lumbar canal stenosis, lower back pain is not so intense and patients exhibit little symptoms during rest, but when they attempt to keep standing up with a straight back or walk, numbness and pain appear in the thighs and in the lower legs down the knees, resulting in difficulty walking. However, when patients take a stooping posture or sit down, the numbness and pain decrease. As the disorder progresses, the lower extremity muscles may weaken, a burning sensation may develop around the anus, difficulty in urination, or turn into urinary incontinence.
Etiology and pathology of lumbar canal stenosis
With advanced age, the spinal canal, through which nerves pass, sometimes gets narrowed because the spine tends to deform, discs may bulge and yellow ligaments thicken, leading to decreased blood flow in the nerves and eventually resulting in the development of lumbar canal stenosis. In addition, intermittent claudication occurs because the spinal canal narrows when you bend backward and it enlarges when you bend forward.
Diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis
 In physical examinations and medical interviews, doctors check if patients have major symptoms of stenosis, such as: presence or absence of intermittent claudication, how far and how long patients can walk before they experience pain, whether or not symptoms are aggravated when they bend backward, how and where symptoms appear, and presence or absence of loss in muscle strength and disturbance of perception.
In physical examinations and medical interviews, doctors check if patients have major symptoms of stenosis, such as: presence or absence of intermittent claudication, how far and how long patients can walk before they experience pain, whether or not symptoms are aggravated when they bend backward, how and where symptoms appear, and presence or absence of loss in muscle strength and disturbance of perception.
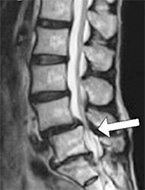
For image diagnostics, X-ray testing and MRI examinations are performed. We cannot decide if a patient has lumbar canal stenosis based only on X-ray testing. But X-ray findings reveal the degree of instability of the lumbar spine and the presence or absence of scoliosis (a sideways curve in the spine). The most important test is MRI. With MRI imaging, we are able to confirm the presence or absence of stenosis and how severe it is.
Prevention and treatment of lumbar canal stenosis
Dos and don’ts in your daily life
You need to maintain a correct posture in your daily life. Since nerve compression increases when you stand up straight and decreases when you bend over, it is recommended that you slightly bend over when walking by using a cane or a walker. Then you can walk easily. Cycling also is a good exercise as it rarely causes pain.
Treatment
Treatment options include rehabilitation, use of a corset, nerve block and medication for improving blood circulation. Oftentimes, symptoms will be improved by these methods. On the other hand, if you still have significant trouble walking and it interferes with your everyday activities, you may need to undergo surgery.
Rehabilitation for lumbar canal stenosis
Improvement of over-bending of the lumbar spine in the standing position
Enhancement of mobility of the hip joint to reduce extension stress on the lumbar spine
Lumbar disc hernia
Symptoms of lumbar disc hernia
Patients with this disorder may feel a pain in the lower back and buttocks with the numbness and pain spreading to the lower legs or they may experience muscle weakness in the lower extremities. The pain may get stronger when you cough or carry a heavy object.
Causes and clinical conditions of lumbar disc hernia
Discs are composed of annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus, serving as cushions in the connection of the backbones. If discs deform and rupture due to aging or any other reason, a part of spinal discs may bulge or distend, compressing nerves and leading to the development of symptoms. Disc hernias tend to be caused by bodily movement or activities done with poor posture, and smoking.
Diagnosis of lumbar disc hernia
The presence of a disc herniation is confirmed by the Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test (the doctor raises the patient’s leg while maintaining the knee in full extension and checks if sciatica appears), and the doctor also sees if the lower extremities become insensitive or if the leg muscles become weakened. In addition, X-ray testing and MRI imaging are conducted to help the doctor to make a precise diagnosis. It should be noted, however, that it is no problem if you are free of symptoms, even when an MRI image shows that a part of your discs sticks out.
Treatment of lumbar disc hernia
During a period of sharp pain, pain reduction procedures are conducted, such as oral administration or suppository insertion of an anti-inflammatory analgesic and nerve block (injection of a drug around the nerve to alleviate pain and inflammation). If the pain subsides, the doctor may order traction therapy and/or exercise therapy. If these methods fail to improve the condition, or the patient complains of weakness of the lower legs or trouble urinating, we may recommend surgery.
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Symptoms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Numbness appears in your hands. You may develop various other symptoms such as difficulty in fastening and unfastening a button, using chopsticks or writing with a pen, or you often find yourself stumbling when walking and you need to hold a handrail on the stairs. Some patients complain of urination problems including frequent urination and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Causes and clinical conditions of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Symptoms are caused by a loss of function in the spinal cord (elevation of discs, formation of a bony spine) due to aging, which lead to compression of the spinal cord inside the canal of the cervical spine.
In comparison with western people, the Japanese have a tendency of developing symptoms of myelopathy because the size of the spinal canal is smaller.
Diagnosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
A diagnosis is made with physical findings including the existence of symptoms and the result of tendon reflexes of the four limbs, also with the observation of a loss of function in the spinal cord in X-ray testing and the presence of compression of the spinal cord in MRI imaging. In a majority of middle-aged and older persons, a loss of function in the spinal cord is observed in X-ray testing and compression of the spinal cord tends to be seen by MRI, even if it is asymptomatic. Therefore, we cannot make a diagnosis based solely on findings of image examinations.
Caution should be exercised as some neurological disorders may exhibit very similar symptoms.
Prevention and treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Patients need to be careful not to fall over, because a slight external injury caused by a fall and other incidents could trigger numbness of four limbs (cord injury).
In general, surgery will be performed if an impaired finger dexterity is observed or if patients need to hold a handrail when they climb up and down the steps. In any case, it is recommended that you visit a medical institution at an early date.